На русском языке:
«Центурион», «Шмель», «Гроза»: какое вооружение получили ВС РБ в 2021 году и что планируют купить сейчас?
На беларускай мове:
«Цэнтурыён», «Шмель», «Навальніца»: якое ўзбраенне атрымалі УС РБ у 2021 годзе і што плануюць купіць зараз?
Belarusian military analyst Yahor Lebiadok published a list of armaments received by the Belarusian Armed Forces in 2021 and the prospects for procurement in 2022. According to the expert, the Belarusian Armed Forces use the method of program-targeted planning for the development of armaments and military equipment. For example, in 2021, a number of key documents were adopted and began to be implemented:
- Armed Forces building and development plan for 2021-2025;
- State armament program for 2021-2025;
- The strategy for the development of the defense sector of the economy of the Republic of Belarus and the State Committee for Military Industry for the period of up to 2025 and the perspective of up to 2030;
- State program for the development of special production for 2022 — 2025.
Rearmament also takes place on the basis of additional narrow programs, such as the concept for the building and development of the Armed Forces communication system up to 2030. Programs of the Union State, for example, on implementation of measures for technical cover of railroads, and programs of military-technical cooperation with the Russian Federation.
The main priorities of armaments purchased by the Belarusian Armed Forces in 2021 are missile and artillery systems, command and communications systems, air defense, reconnaissance, electronic warfare, UAV, and means to counter them.
«According to the State Secretary of the Security Council Volfovich, more than 30% of weapons and equipment in the Armed Forces of Belarus are Belarusian-made. But it is not clear what he is talking about – nomenclature, quantity, or in terms of value,» Lebiadok writes.
Last year, more than 35 nomenclatures of weapons, military and special equipment were accepted for service. Among them, more than 600 units of new weapons, military and special equipment, as well as auxiliary equipment were supplied to the Armed Forces by the organizations of the State Committee for Military Industry.
What weapons did the Belarusian Armed Forces receive in 2021?
Ground Forces
- 7,62-mm VSK-100 assault rifle;
- 7,62-mm AKMS-MB assault rifle;
- 6 MZKT-741501 road trains;
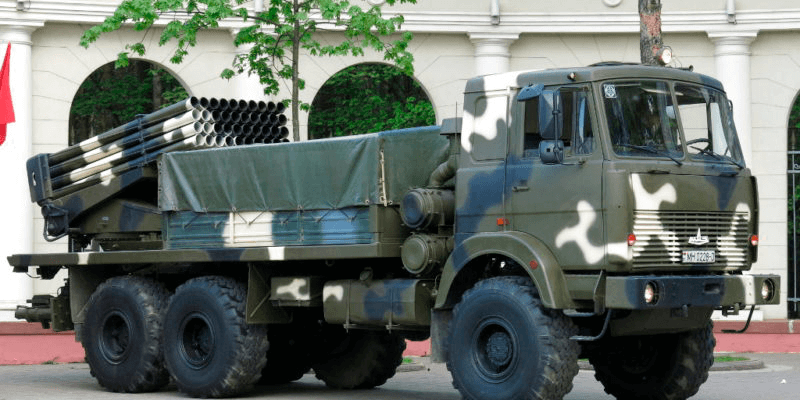
- BM-21B Belgrad-2 multiple rocket launcher.
BM-21B Belgrad-2 multiple rocket launcher / belvpo
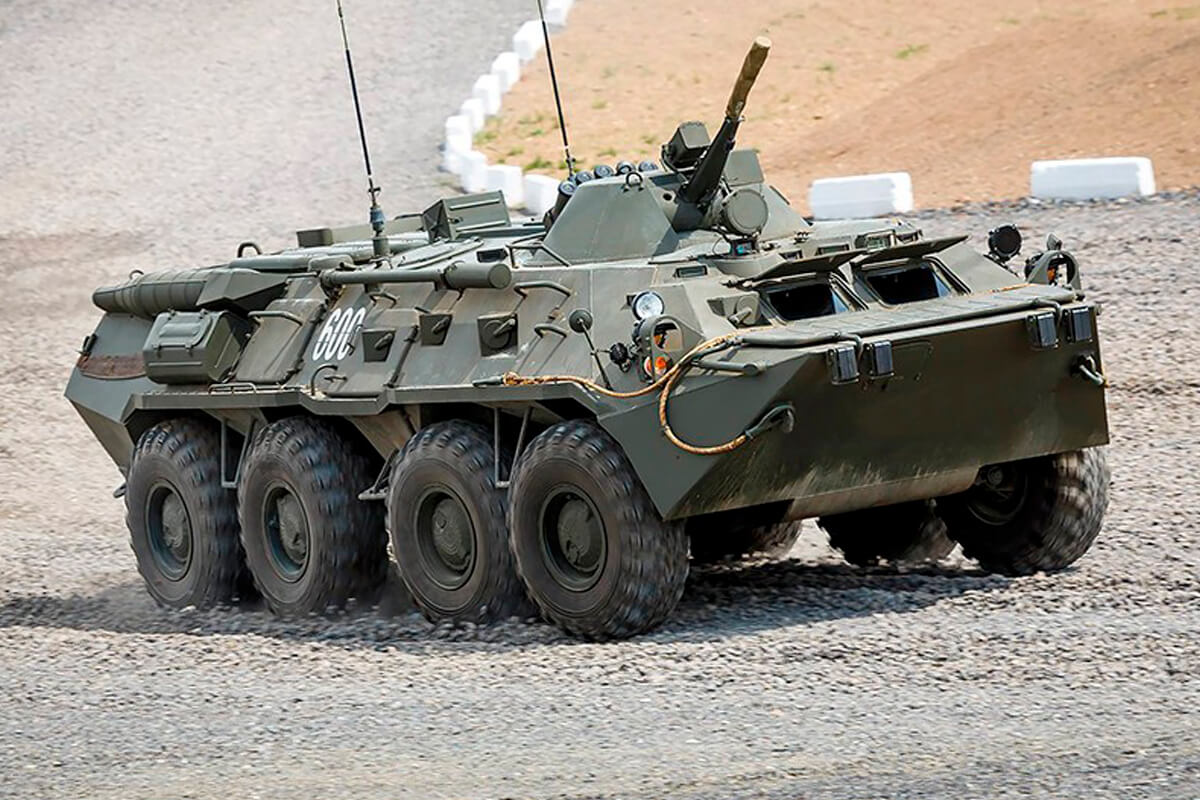
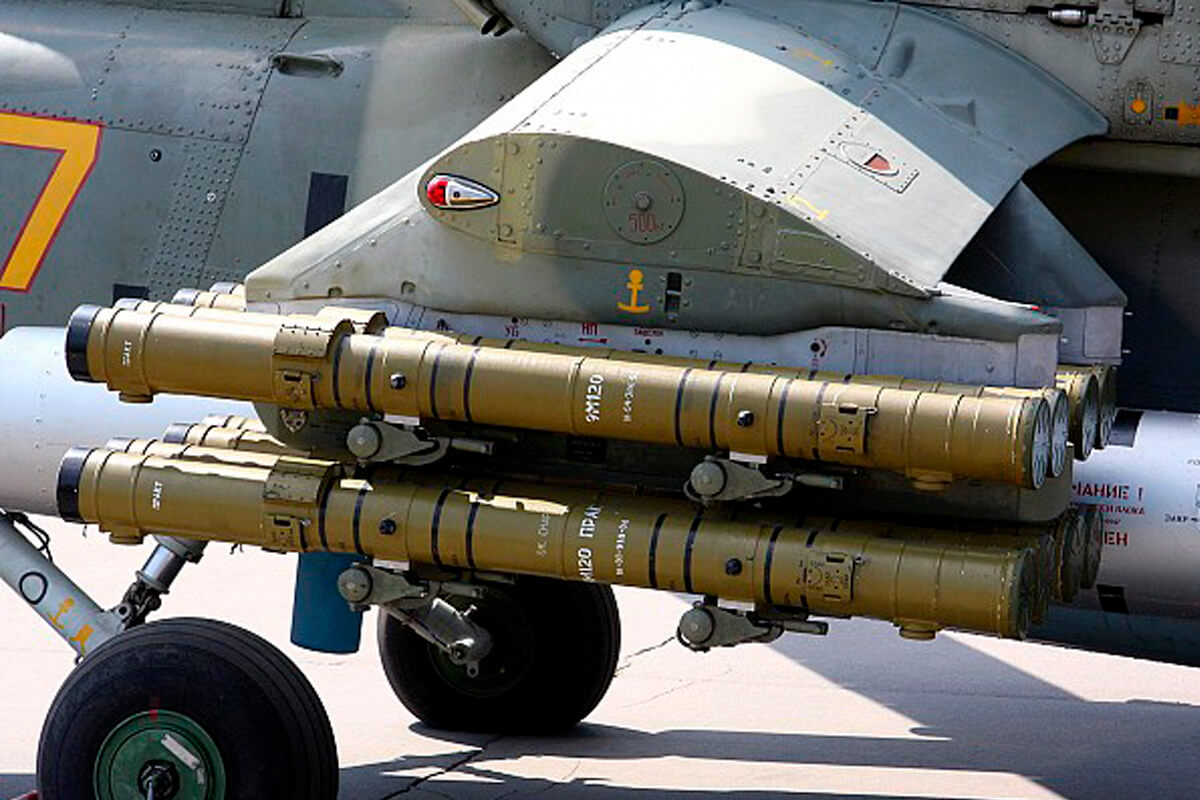
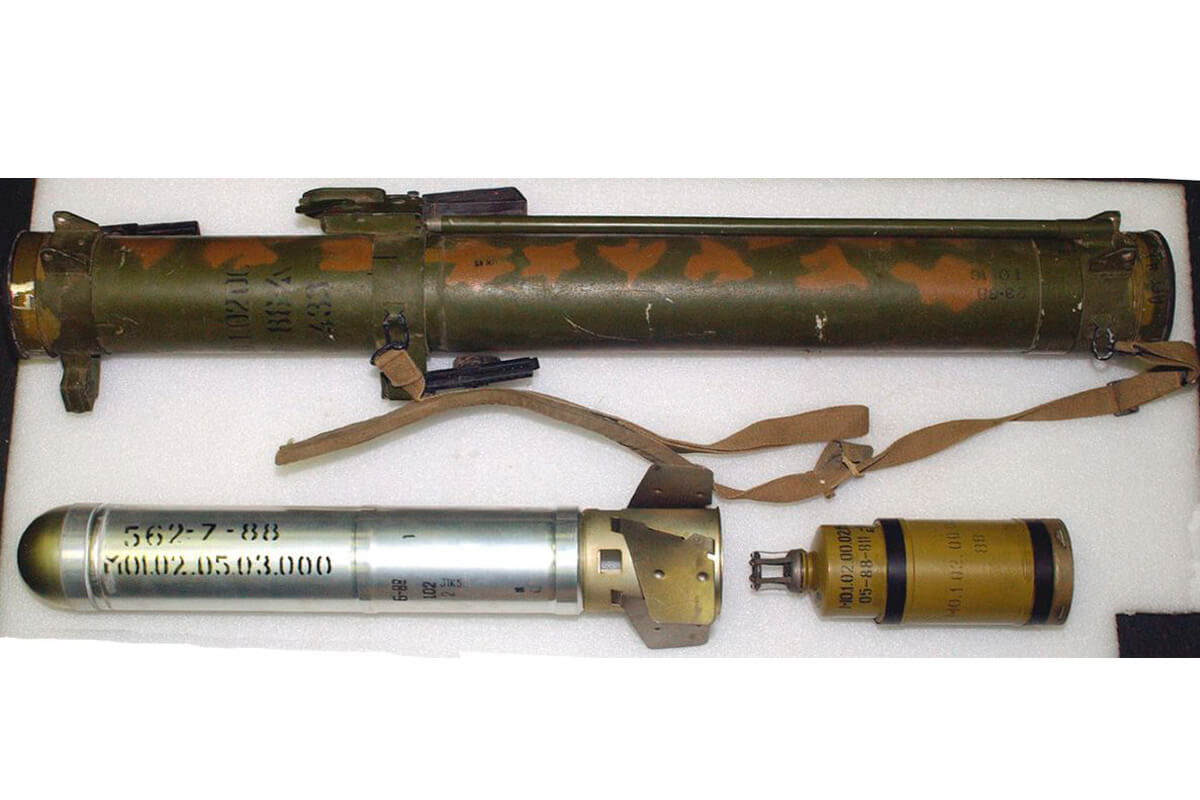
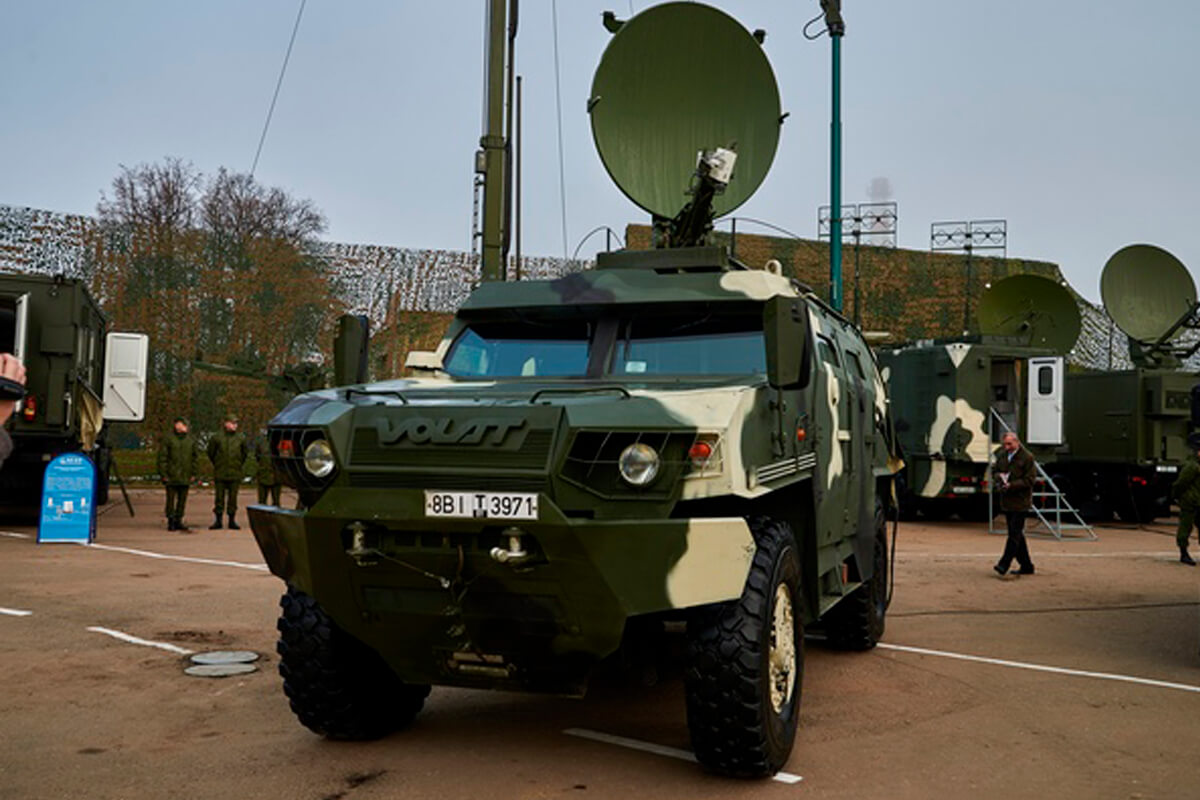
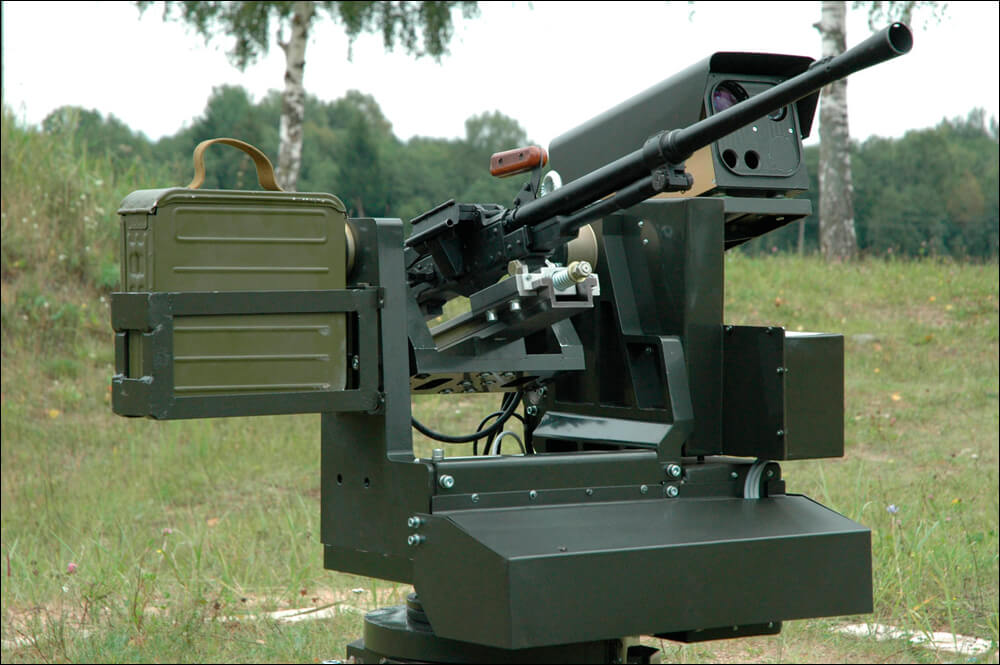
OJSC Agat — Electromechanical Plant supplied a batch of Tsenturion artillery fire control command vehicles to the Armed Forces. Two battalion sets of BTR-82A armored personnel carriers, BTR-80K command vehicles, and BMM armored ambulance were supplied to the Belarusian Armed Forces from Russia. A batch of Russian 9M120 Ataka anti-tank guided missiles was delivered, and the purchase of Russian RPO-A Shmel man-portable rocket-assisted flamethrowers continued.
Signal corps
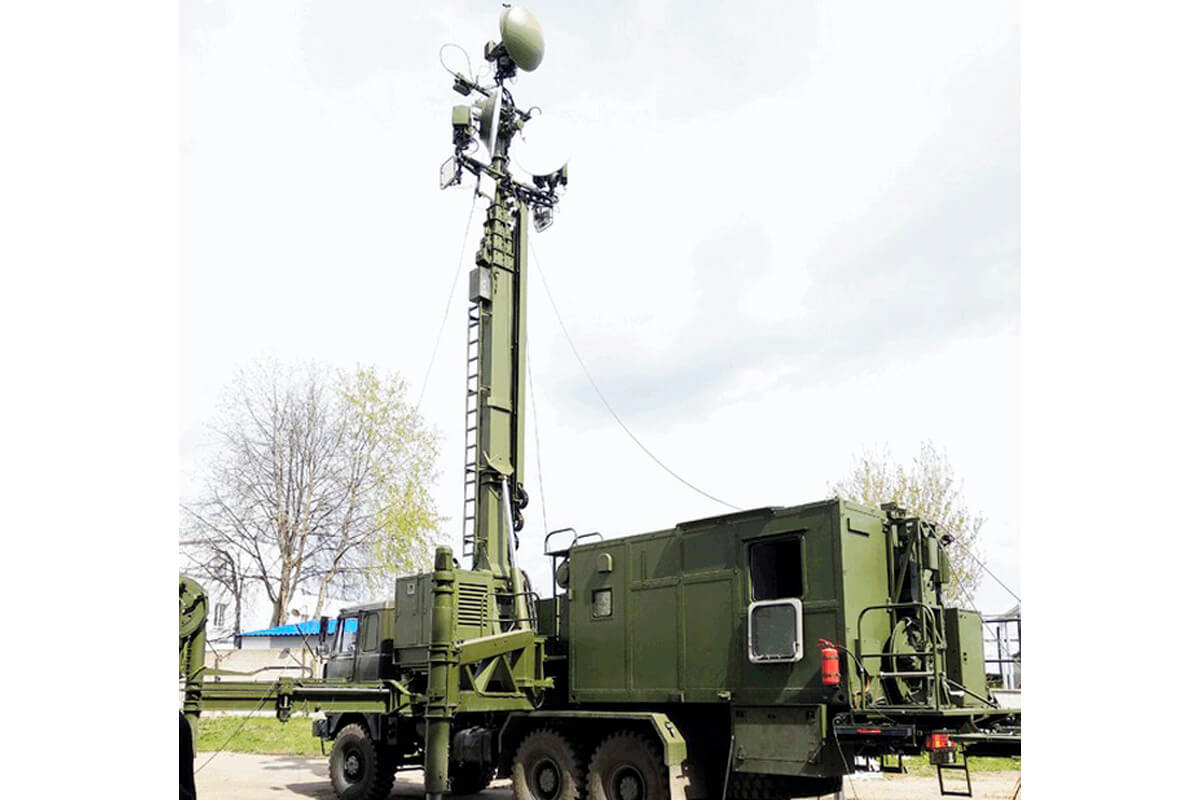
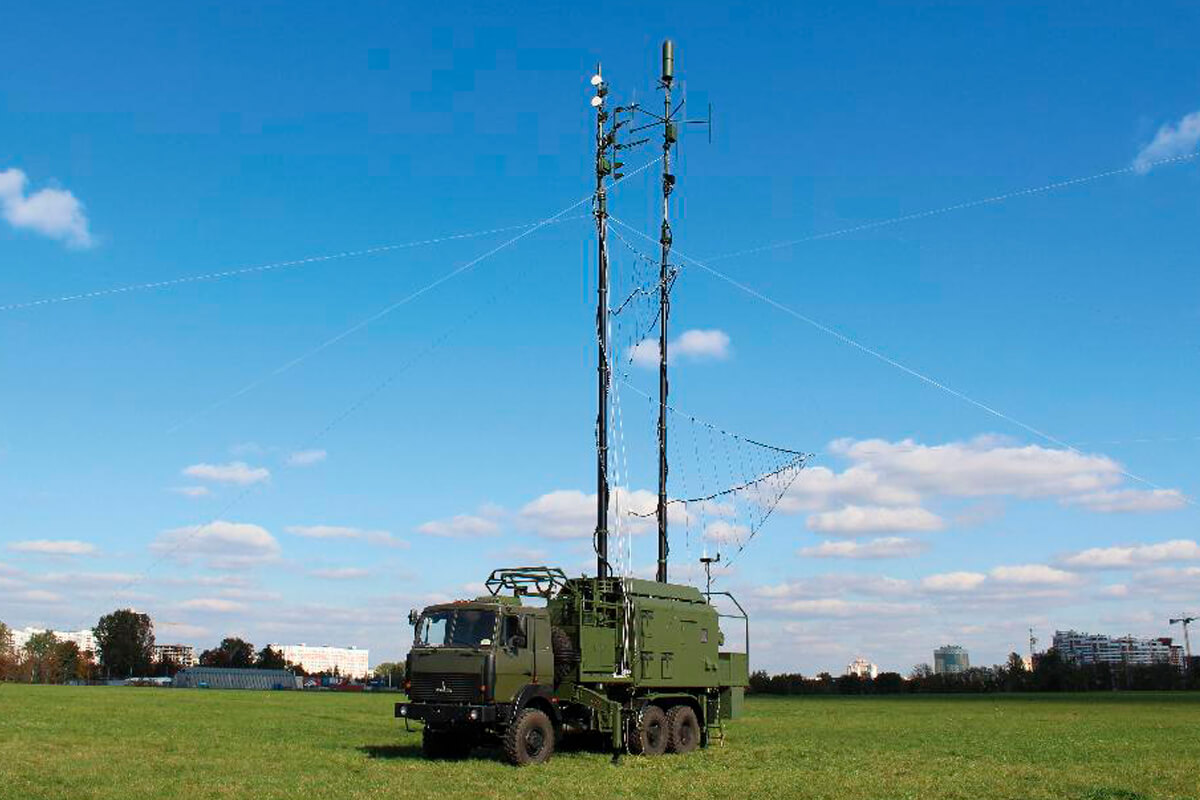
In 2021, more than 374 units of communication equipment, 120 sets of fiber-optic cable, 26 units of technical support equipment for information support of the Armed Forces, and 20 sets of encryption equipment were supplied to the Armed Forces of Belarus by the organizations of the State Committee for Military Industry. Among them:
- R-434 Citrus radio relay station;
- R-414MBRP Sosna-2 radio relay station;
- R-409MB-1 upgraded radio relay station.
- R-186 Bogatyr-2 and R-186D Drakon combined radio stations;
- P-240MB Kaiman-KAS integrated communication control equipment;
- R-144UMB communication center;
- automated reconnaissance, control and communication complexes Pustelga.
According to the analyst, the equipping of the communications troops with new communication equipment made it possible to complete the transition to digital information communication systems at the strategic and operational levels and to continue the transition activities at the tactical level.
Electronic warfare, Radio relay stations, Communications intelligence
The Armed Forces received: 1 Rosa RB radar system, 2 R-934UM2 Groza-6 jamming stations and 4 anti-UAV radio electronic guns (KB-Radar). In addition, in 2021, the Ministry of Defense was planning to purchase Russian Torn-8P radio control system, but there is no information on the results of the purchase.
In addition to mentioned above, hardware and software complexes Sphere, designed for detection, direction finding and suppression of control and navigation channels of commercial UAVs of multicopter type through jamming in the frequency bands of UAV control and navigation channels were mastered by the Belarusian Armed Forces. Also, jamming station Egida was tested in a training battle to suppress numerous nano-, micro- and mini-class drones.
System Mirazh, designed to protect ground objects of armaments, military and special equipment from airborne radar reconnaissance through automatic formation of simulating and masking jamming onboard radar stations of reconnaissance and attack aircraft, as well as UAVs, is being tested. The share of modern electronic warfare equipment in military units and electronic warfare units of the Belarusian Armed Forces in 2021 was more than 50%.
UAV and robotic systems
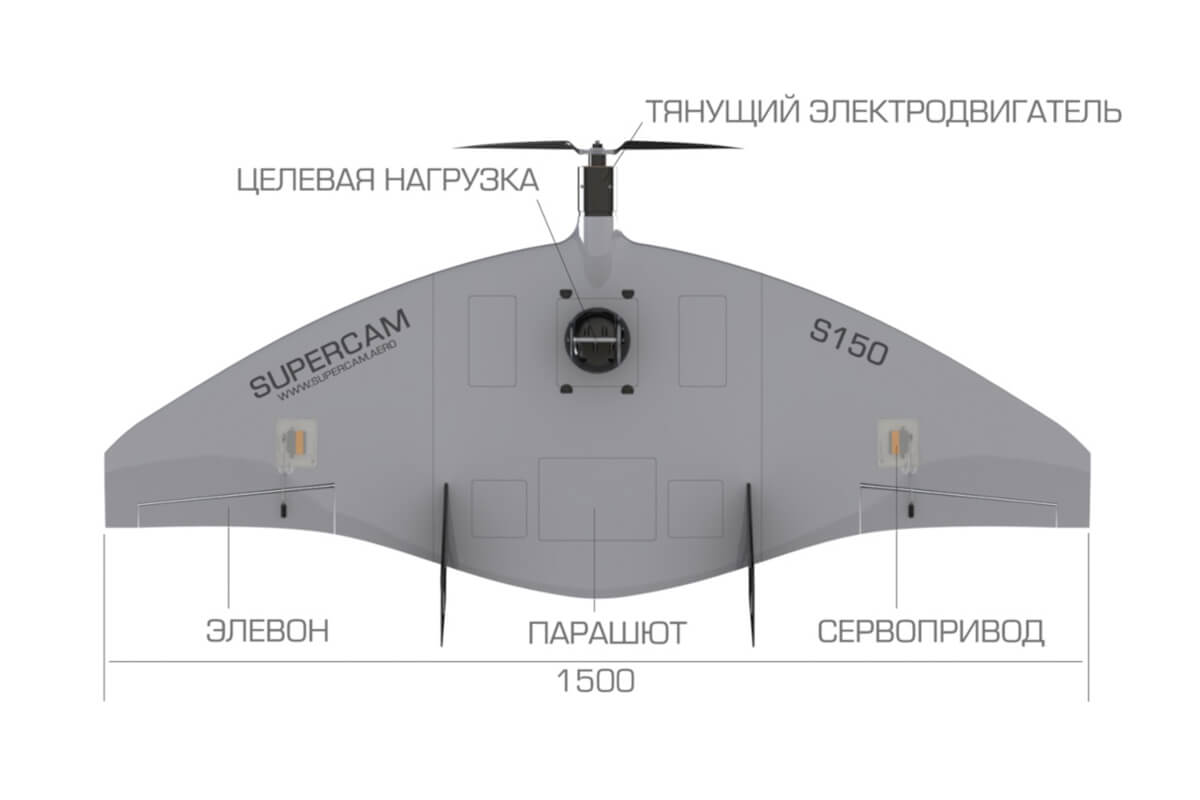
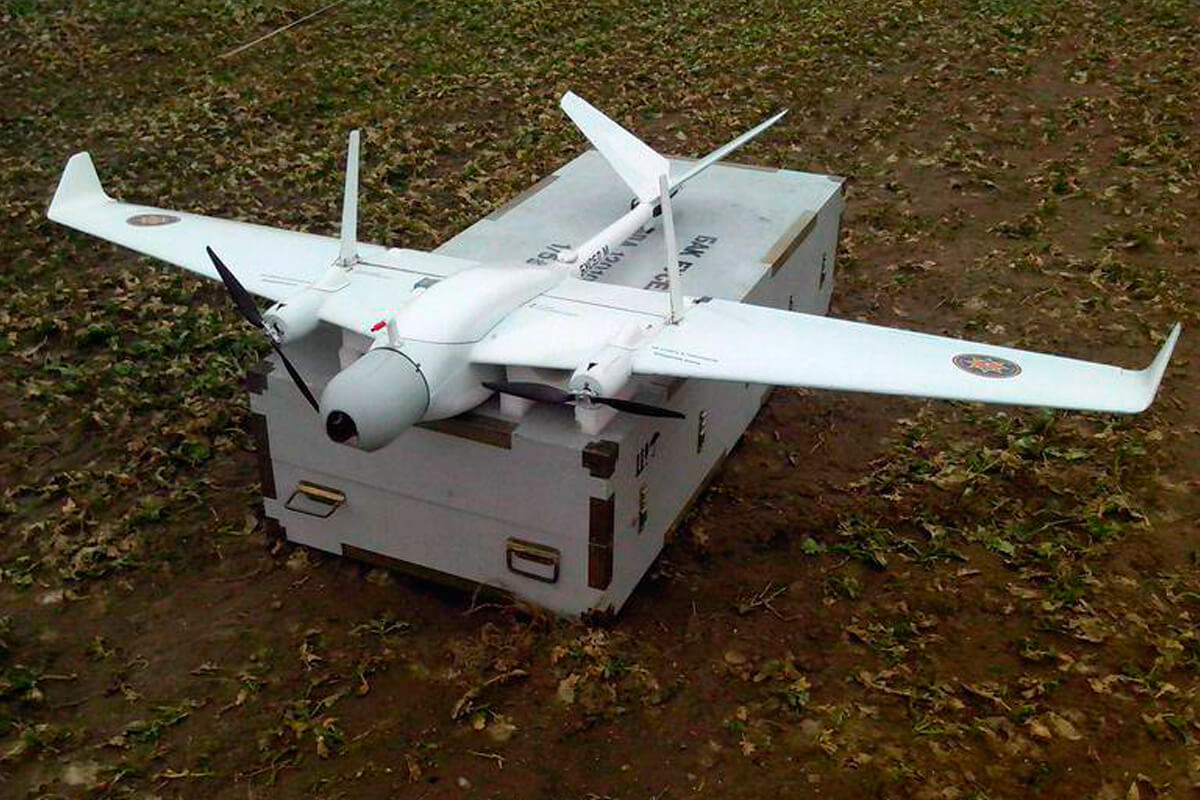
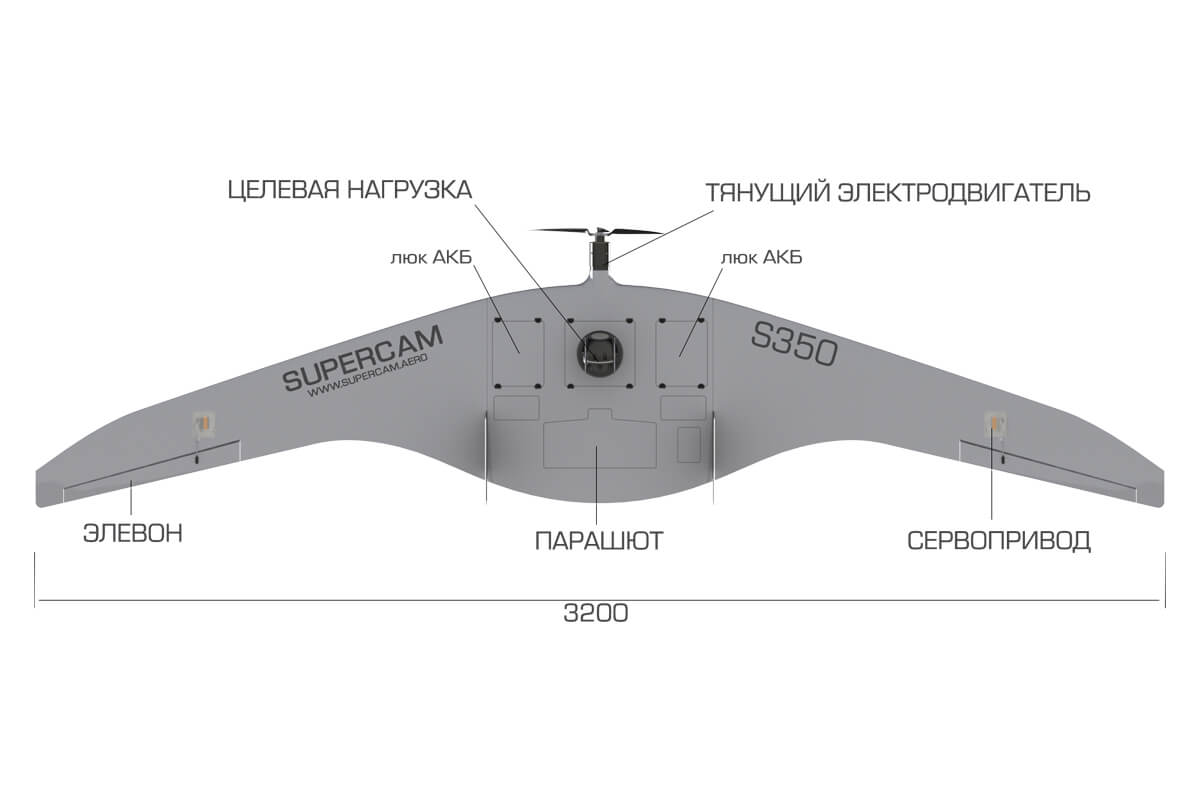
Russian Superkam S150 and Superkam S350 UAVs continue to be purchased. In 2021, the Ministry of Defense was planning to purchase a tactical navigation system with Busel-10 UAV.
It is especially worth noting that 4 automated remotely-controlled observation and fire systems Adunok (the manufacturer is KB Display) have been accepted for service. Belarus has developed a number of ground robotic systems (Adunok, Berserk, Bogomol, Vistl, MRK-A1), but there were problems with their acceptance for the following reasons:
- The military specialists’ lack of understanding of the place, role and purpose of robotic weapon systems in the Armed Forces and, as a consequence, the real needs for them;
- Absence of a single scientifically justified and regulated procedure for creating, developing and implementing robotic systems;
- Management activities in the Armed Forces on robotization are not centralized on the proper level.
In 2021, the situation seems to have improved.
Automated remotely-controlled observation and fire systems Adunok / robotrends.ru
Engineering Corps and Logistic Support
In 2021, DEM-310 excavator-loaders, universal Amkodor-352 S loaders, 16 KS-55727-5 truck cranes, as well as metal detectors and diving equipment were supplied to the engineering corps of the Belarusian Armed Forces.
The 83rd airfield engineering regiment of the Air Force and Air Defense Forces received KO-806 combined cleaning machine and Amkodor 6712V vibratory roller. Also, five mobile laundry modules of a container type PPM(K) were purchased, and flexible fuel storage tanks were accepted for the provision.
Amid the gradual transition to the wearing of new items of casual and combat clothing by servicemen serving under contracts, they began to provide conscript soldiers with new winter jackets, olive-colored underwear, and berets. A mobile field warehouse was produced and accepted for the provision to the Armed Forces.
Repair and modernization
In the past year, the enterprises of the State Committee for Military Industry restored more than 60 units of armaments and military equipment in the interests of the Armed Forces. This included the repair of six aircraft, the major repairs of one helicopter and S-300 PS system. From 2019 to September 2021, 180 R-27 air-to-air missiles were repaired and delivered into service in the interests of the military department. Military repair agencies have repaired more than 4,500 armaments and military equipment.
R-27 air-to-air missile / missilery.info
Russia has conducted major repairs of two batteries of 2S3M self-propelled howitzers. Like in the BTR-82A, the communication equipment in them is Belarusian. JSC Kidma-Tek carried out modernization of 9M114BM Rumba supersonic anti-tank missile and modernized a new electronic compartment of MK-80BM infrared seeking head with application of modern radio-electronic element base for R-73 short-range air-to-air missile, which were launched from MiG-29 and Yak-130 aircraft.
Since the beginning of the year, the specialists of the 1371st engineering base have repaired more than 90 units of engineering equipment, more than half of them are hoisting machines, track laying equipment and positioning equipment, and bulldozers.
Armament procurement plan for 2022
After the tests are completed, it is planned to deliver the Vostok three-axis radar system, the serial modernization of Grad and Uragan multiple rocket launchers, the arrival of sights and equipment, the Quadro-1400 and the Barrage Tube UAVs for the Special Operations Forces.
In September 2021, A. Lukashenka said that Belarus was planning to buy more than $1 billion worth Russian armaments. This is about purchases in the coming years. Among them:
- Su-30SM aircraft (4 aircraft are expected to be delivered under an existing contract);
- Mi-35 helicopters (probably already delivered, at least this type was assigned the letter Q of the state aircraft type registration mark on March 15, 2022 by Decree No. 17 of the Ministry of Defense of Belarus);
- 12A6 Sopka-2 track radar system;
- Protivnik-G radio relay station;
- Tor-M2 surface-to-air missile system;
- BTR-82A for the Special Operations Forces of Belarus;
- Negotiations were held to supply the S-400 surface-to-air missile system.
It should be noted that the supply of serious armaments such as S-400 or Iskander missile systems to the Republic of Belarus is regulated by the Russian law in the same way as to other foreign states – by the decision of Putin.
«From the point of view of military and political thinking of the Russian leadership, it makes more sense for them to place such weapons in Belarus to ensure the security of the Union State and to manage them themselves, rather than to hand them over to Belarus (especially in the conditions of war and political games of Lukashenka). This is what we saw in 2021. This is also caused by the economic situation – Belarus, unlike, for example, Azerbaijan, buys Russian serious armaments on credit. And the economic situation in the coming years will be difficult both in Belarus and Russia,» the expert says.
The complication of Russian armament supplies may be related to losses of the Russian Armed Forces in Ukraine. For example, as of 11.05.2022, Russia has lost about 5 Su-30SM aircraft, 3 Mi-35 helicopters (and 3 Mi-24), 153 units of BTR-82A. Therefore, its main priority may be the completion of its Armed Forces, rather than deliveries on credit to an ally.